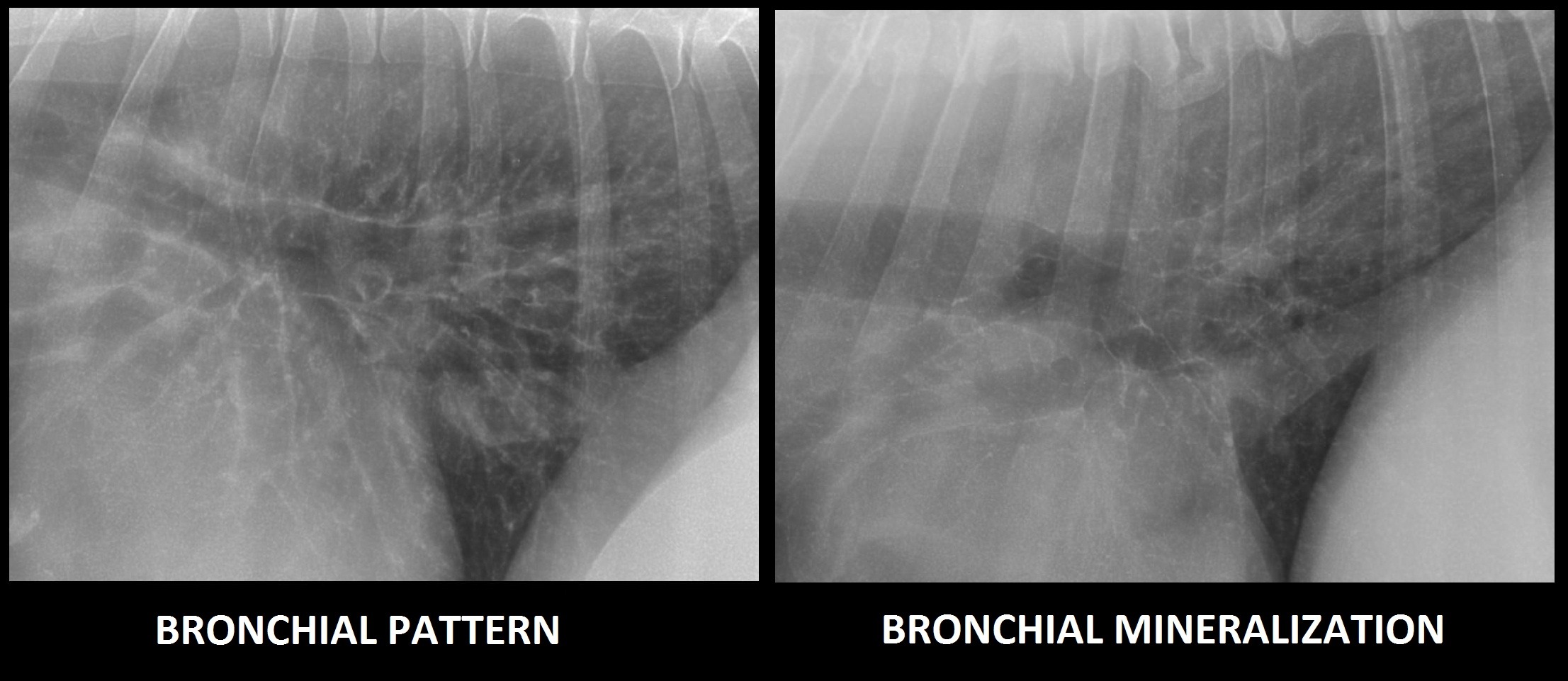
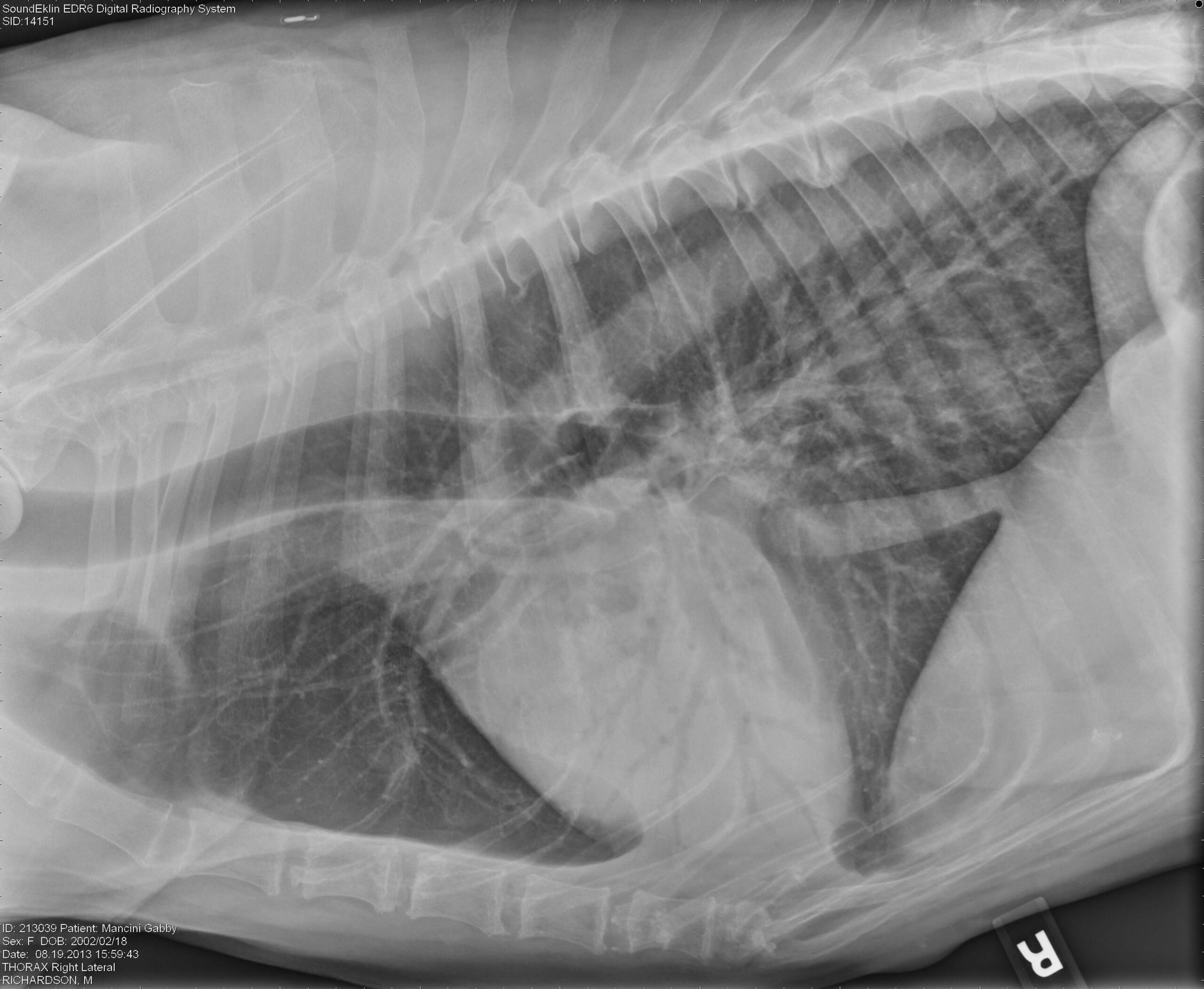
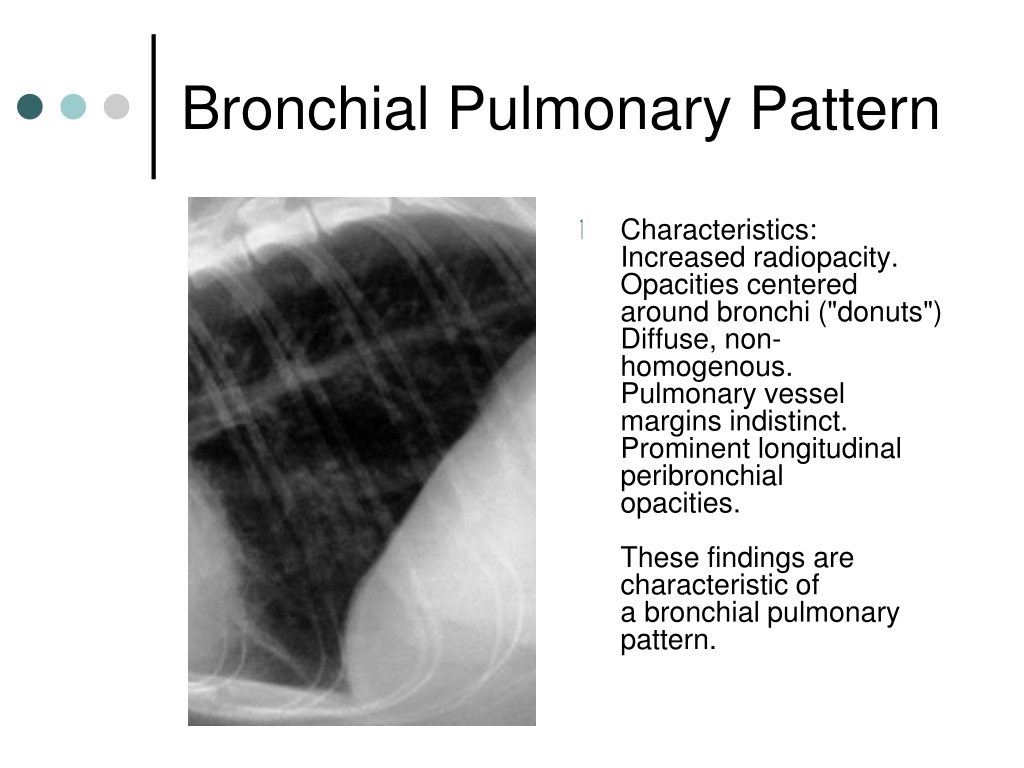
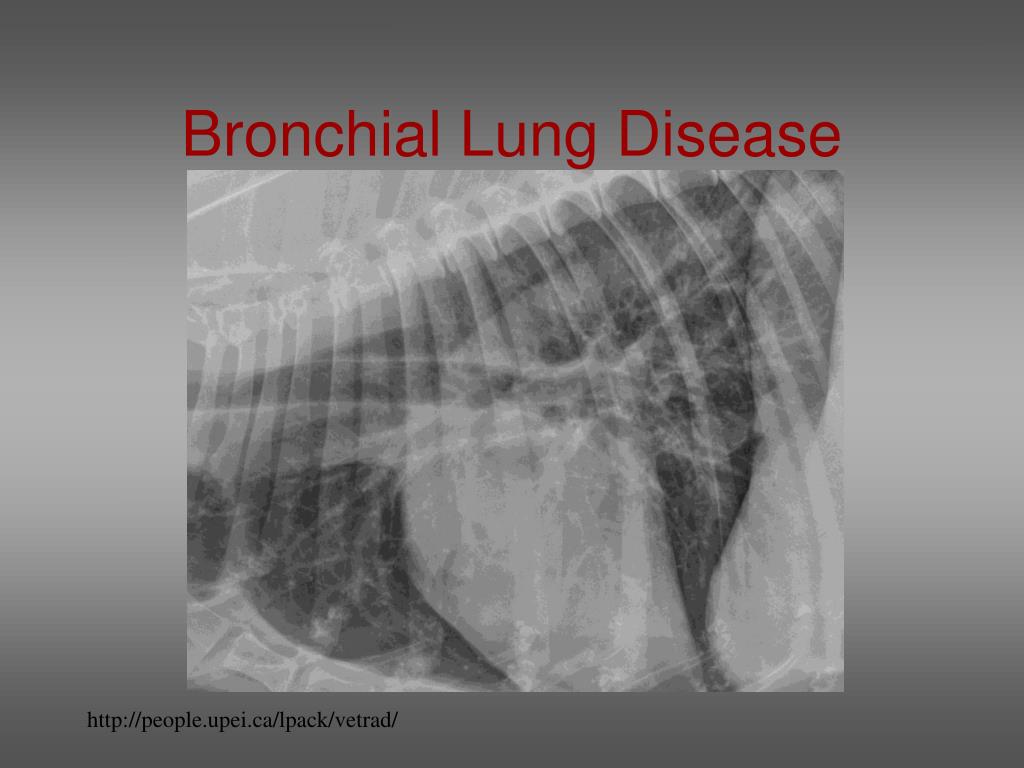
Bronchial Pattern Dog
Bronchial Pattern Dog - Web bronchial lung pattern the bronchial pattern is obtained when the bronchial wall is infiltrated by cells or fluid or when the peribronchial space is replaced by cells or fluid. Web when a dog breathes in, air flows through their mouth or nose to their trachea, also known as the windpipe. Diffuse interstitial or alveolar patters may be due to vasculitis, acute lung injury (ali), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), atypical pneumonia, or neoplasia such as lymphoma. Web tracheobronchitis is a sudden or longterm inflammation of the trachea and bronchial airways; He had no known travel history or recent exposure to other dogs, and he was current on vaccinations and heartworm preventive. Web diffuse pulmonary disease may be in the form of a bronchial pattern, or interstitial or alveolar pattern. Dogs and cats with respiratory tract disorders can present to veterinarians for a variety of clinical signs including nasal discharge, sneeze, reverse sneeze, noisy breathing (snoring/stertor, stridor, wheeze), cough, alterations in respiratory rate or effort, and respiratory distress. If the cough lasts more than two months, it's generally referred to as chronic bronchitis. Web a bronchial pattern on radiographs indicates a condition that involves the airways. Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. Diffuse interstitial or alveolar patters may be due to vasculitis, acute lung injury (ali), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), atypical pneumonia, or neoplasia such as lymphoma. Also see professional content regarding tracheobronchitis. Web b) bronchial patterns: To understand the disease, it's first important to know about the basic anatomy that's involved. Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. If the cough lasts more than two months, it's generally referred to as chronic bronchitis. Web bronchial patterns are generally distinct from interstitial and alveolar patterns, with the primary cause being thickening of the larger, conducting airways. It can be a subtle pattern to recognize, so lets look at some of the features. Web bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial airways that may extend into the lungs. It often occurs in dogs already affected by respiratory disease or a disorder of the lungs or airways. Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. A bronchial pattern is an abnormal lung opacity caused by peribronchial cellular, fluid and fibrotic infiltration, or bronchial mucosal and submucosal thickening (chronic bronchitis). Web b) bronchial patterns: Yellow circles) and parallel lines (“tramlines”; To understand the disease, it's first important to. It may also extend into the lungs. This does not hold true in the cat. Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well as the keys to interpreting the meaning of these patterns. Bacterial > allergic (eosinophilic) cats: The walls are thickened due to a combination of smooth muscle hypertrophy, mucus. A bronchial pattern is an abnormal lung opacity caused by peribronchial cellular, fluid and fibrotic infiltration, or bronchial mucosal and submucosal thickening (chronic bronchitis). The thickening of those structures results in enhanced radiographic visualization of. This makes them easier to see, especially in the periphery of the lung (image 2). This does not hold true in the cat. Also see. Bacterial > allergic (eosinophilic) cats: Typically, neither the esophagus nor tracheobronchial lymph nodes are visualized in thoracic radiographs from. Web bronchitis in dogs is a common illness that affects the upper airways and causes coughing. This does not hold true in the cat. Web a bronchial pattern on radiographs indicates a condition that involves the airways. Web when a dog breathes air in through its nose or mouth, the air travels down the trachea, which divides into the tubes known as the right and left bronchi, then into the smaller airways called bronchioles in the lungs. Diffuse interstitial or alveolar patters may be due to vasculitis, acute lung injury (ali), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), atypical. Web bronchial lung pattern the bronchial pattern is obtained when the bronchial wall is infiltrated by cells or fluid or when the peribronchial space is replaced by cells or fluid. Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well as the keys to interpreting the meaning of these patterns. Perihilar distribution (in. Web bronchitis in dogs is a common illness that affects the upper airways and causes coughing. It is discussed in this chapter as part of tracheobronchitis. It may also extend into the lungs. Bacterial > allergic (eosinophilic) cats: This pattern comes closest to helping shed light on what disease the pet is suffering from. Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well as the keys to interpreting the meaning of these patterns. In a true bronchial pattern that stems from infectious/inflammatory disease, the bronchial walls are thickened because of inflammatory tissue and cells surrounding the airways. Also see professional content regarding tracheobronchitis. Diffuse interstitial or. Also see professional content regarding tracheobronchitis. It often occurs in dogs already affected by respiratory disease or a disorder of the lungs or airways. This pattern comes closest to helping shed light on what disease the pet is suffering from. Web b) bronchial patterns: A bronchial pattern is an abnormal lung opacity caused by peribronchial cellular, fluid and fibrotic infiltration,. It often occurs in dogs already affected by respiratory disease or a disorder of the lungs or airways. Cranioventral distribution is most associated with bronchopneumonia; He had no known travel history or recent exposure to other dogs, and he was current on vaccinations and heartworm preventive. Web bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial airways that may extend into the. In a true bronchial pattern that stems from infectious/inflammatory disease, the bronchial walls are thickened because of inflammatory tissue and cells surrounding the airways. Also see professional content regarding tracheobronchitis. To understand the disease, it's first important to know about the basic anatomy that's involved. Web alveolar patterns are typically fluffy and indistinct, and coalesce. He had no known travel history or recent exposure to other dogs, and he was current on vaccinations and heartworm preventive. It may also extend into the lungs. Web bronchitis in dogs is a common illness that affects the upper airways and causes coughing. Web bronchial patterns are generally distinct from interstitial and alveolar patterns, with the primary cause being thickening of the larger, conducting airways. Typically, neither the esophagus nor tracheobronchial lymph nodes are visualized in thoracic radiographs from. Yellow circles) and parallel lines (“tramlines”; The trachea then carries the inhaled air to the bronchi (the tubes that connect the. This pattern comes closest to helping shed light on what disease the pet is suffering from. What are the signs of chronic bronchitis? Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well as the keys to interpreting the meaning of these patterns. Diffuse interstitial or alveolar patters may be due to vasculitis, acute lung injury (ali), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), atypical pneumonia, or neoplasia such as lymphoma. A bronchial pattern is an abnormal lung opacity caused by peribronchial cellular, fluid and fibrotic infiltration, or bronchial mucosal and submucosal thickening (chronic bronchitis).Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
Interpreting thoracic radiograph lung patterns VETgirl Veterinary
Chronic & Persistent Coughing in a Dog Clinician's Brief
PPT Veterinary Radiology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of lung lesions in
Thoracic radiograph of dog showed mild bronchial pattern (A) and an
Imaging the Coughing Dog
PPT Thoracic Radiology of the Dog PowerPoint Presentation, free
Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of lung lesions in
Web B) Bronchial Patterns:
Web Diffuse Pulmonary Disease May Be In The Form Of A Bronchial Pattern, Or Interstitial Or Alveolar Pattern.
Web When A Dog Breathes Air In Through Its Nose Or Mouth, The Air Travels Down The Trachea, Which Divides Into The Tubes Known As The Right And Left Bronchi, Then Into The Smaller Airways Called Bronchioles In The Lungs.
Web Bronchitis Is An Inflammation Of The Bronchial Airways That May Extend Into The Lungs.
Related Post: