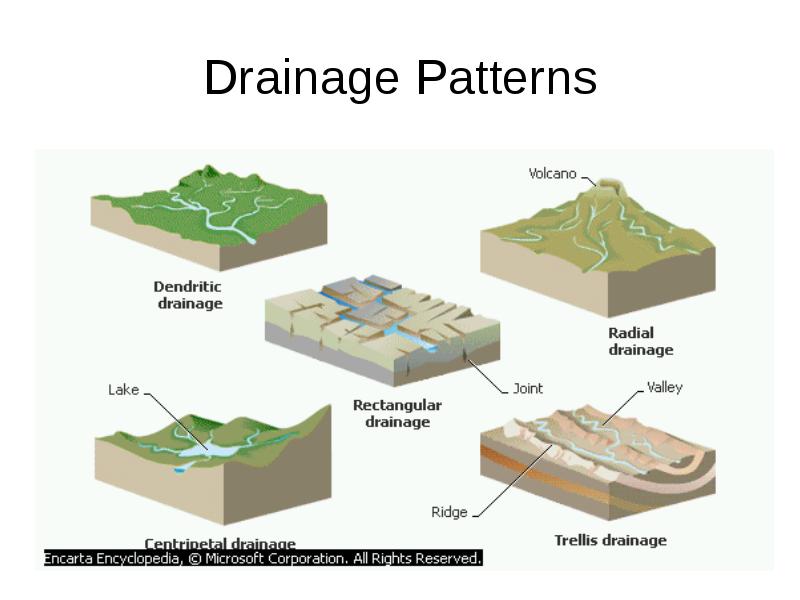
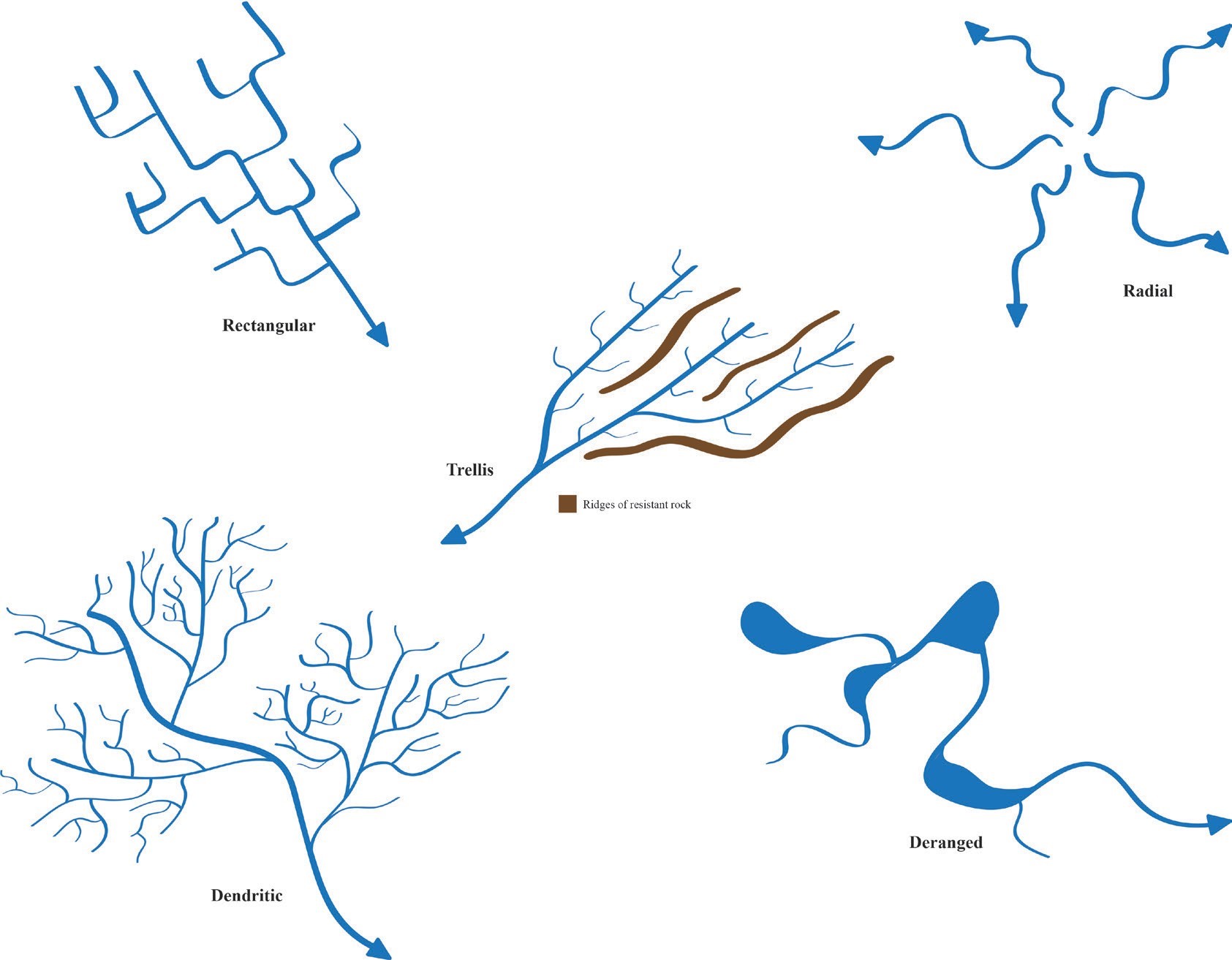
Centripetal Drainage Pattern
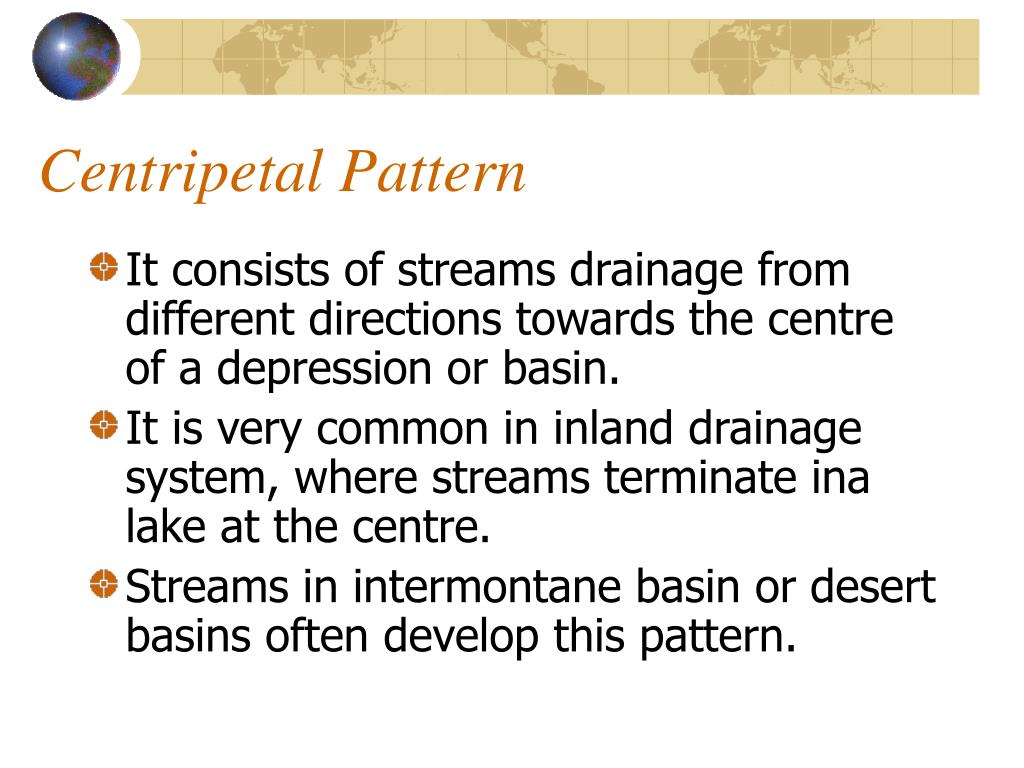
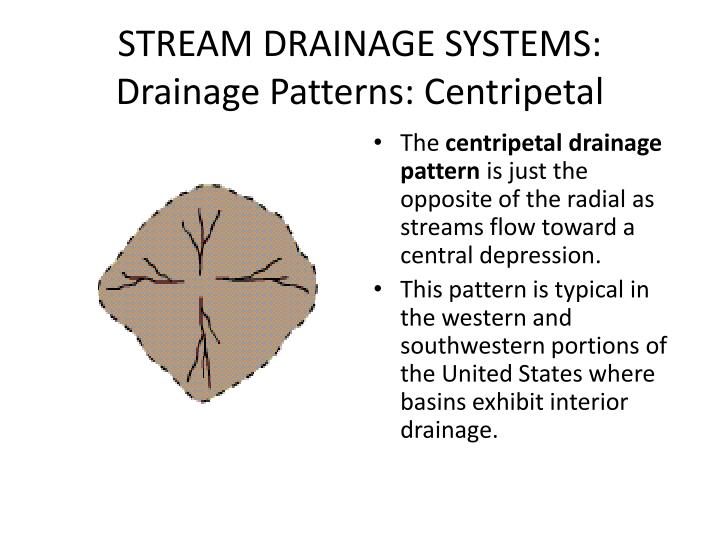
Centripetal Drainage Pattern - These streams feed ephemeral lakes that evaporate during dry spells throughout the wetter parts of the year. Nited states where basins exhibit interior drainage. Drainage basin morphometry can be quantified by several parameters, including: Most river patterns evolve through natural selection. Web at site and sector scale, channel morphology varies spatially and in time, but river patterns and drainage texture, or the frequency of stream lines per unit area, together determine the intricacy, or otherwise, of topography. Streams follow the path of least resistance and thus are concentrated in places were exposed rock is the weakest. Sambhar basin has a centripetal drainage pattern as streams drain towards the lake. Web the pattern of tributaries within a drainage basin depends largely on the type of rock beneath, and on structures within that rock (folds, fractures, faults, etc.). Rivers radiate outward from a central peak, seen in the deccan plateau. Streams diverge from a central elevated tract: Web centripetal patterns are produced where drainage converges on a single outlet or sink, as in some craters, eroded structural domes with weak cores, parts of some limestone country, and enclosed desert depressions. During wetter portions of the year, these streams feed ephe. Web centripetal drainage pattern: Rivers converge towards a central basin, like in the thar desert. Centripetal or inland drainage pattern (fig. The centripetal pattern is noted in craters, calderas, structural basins and breached domes (relief inversion). Streams follow the path of least resistance and thus are concentrated in places were exposed rock is the weakest. Web centripetal drainage pattern. During wetter portions of the year, these streams feed ephemeral lakes, which evaporate away during dry periods. Distribution of stream courses and their spatial relationship to one another. Rivers radiate outward from a central peak, seen in the deccan plateau. Drainage lines converge into a central depression, like a sinkhole, crater, or other basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. 17.11) is opposite to the radial drainage pattern because. During wetter portions of the year, these streams feed ephemeral lakes, which evaporate away during dry periods. All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns ( fig. 17.11) is opposite to the radial drainage pattern because it is characterized by the streams which converge at a point which is generally a depression or a basin. Streams. Centripetal or inland drainage pattern (fig. Nited states where basins exhibit interior drainage. Web the pattern of tributaries within a drainage basin depends largely on the type of rock beneath, and on structures within that rock (folds, fractures, faults, etc.). It is mainly fed by four streams namely mendha, rupangarh, kharain and khandel. They are governed by the topography of. Web centripetal drainage pattern. Streams follow the path of least resistance and thus are concentrated in places were exposed rock is the weakest. The streams produce a centripetal or inland drainage pattern when they converge at a place, which is usually a depression or basin. Domes, volcanic cones, isolated conical hills. Sambhar basin has a centripetal drainage pattern as streams. This pattern is typical in the western and southwestern portions of the. When rivers discharge their waters from all directions in a lake or depression, the pattern is known as ‘centripetal’. Streams follow the path of least resistance and thus are concentrated in places were exposed rock is the weakest. Web in geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems,. Web centripetal drainage pattern, also known as an endorheic drainage system, exhibits a distinct hydrological characteristic: Web the pattern of tributaries within a drainage basin depends largely on the type of rock beneath, and on structures within that rock (folds, fractures, faults, etc.). All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns ( fig. Rivers radiate outward. It is mainly fed by four streams namely mendha, rupangarh, kharain and khandel. Web in geomorphology, a drainage system is the pattern formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. Nited states where basins exhibit interior drainage. Most river patterns evolve through natural selection. Web in the radial outward pattern, drainage lines radiate out from a. Most river patterns evolve through natural selection. During wetter portions of the year, these streams feed ephe. Domes, volcanic cones, isolated conical hills. Web centripetal drainage pattern. Drainage pattern which looks like tree branches is known as dendritic drainage pattern. Sambhar basin has a centripetal drainage pattern as streams drain towards the lake. Domes, volcanic cones, isolated conical hills. Drainage basin morphometry can be quantified by several parameters, including: The three main types of drainage patterns are illustrated in figure 13.7. Rivers radiate outward from a central peak, seen in the deccan plateau. This pattern is typical in the western and southwestern portions of the united states where basins exhibit interior drainage. The centripetal pattern is noted in craters, calderas, structural basins and breached domes (relief inversion). Web centripetal drainage pattern, also known as an endorheic drainage system, exhibits a distinct hydrological characteristic: Rivers converge towards a central basin, like in the thar. Web centripetal patterns are produced where drainage converges on a single outlet or sink, as in some craters, eroded structural domes with weak cores, parts of some limestone country, and enclosed desert depressions. Web centripetal drainage pattern. 17.11) is opposite to the radial drainage pattern because it is characterized by the streams which converge at a point which is generally a depression or a basin. Streams follow the path of least resistance and thus are concentrated in places were exposed rock is the weakest. When rivers discharge their waters from all directions in a lake or depression, the pattern is known as ‘centripetal’. India’s four drainage patterns are: Streams diverge from a central elevated tract: Web in geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. It is similar to the radial drainage system, with the only exception that radial drainage flows out where as the centripetal drainage flows in. They are governed by the topography of the land, whether a particular region is dominated by. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Web centripetal drainage pattern, also known as an endorheic drainage system, exhibits a distinct hydrological characteristic: Sambhar basin has a centripetal drainage pattern as streams drain towards the lake. These streams feed ephemeral lakes that evaporate during dry spells throughout the wetter parts of the year. This pattern is typical in the western and southwestern portions of the united states where basins exhibit interior drainage. This pattern is typical in the western and southwestern portions of the.Centripetal Drainage Pattern
The Water Cycle The Longitudinal Profile
River & Drainage Patterns Types Of Drainage Facts
Overview of Water Introductory Physical Geology Laboratory Manual
अपकेंद्रीय ( रेडियल) और अभिकेंद्री (सेंट्रिपेटल ) अपवाह प्रारूप के बीच
Structural Control of Landforms Mostly Chapter 12 Plus
Distinction between centripetal drainage of the dome flank system
PPT Drainage Basin PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6398776
PPT DYNAMIC EARTH’S FRESH WATERS PowerPoint Presentation ID
Centripetal Drainage Pattern
Web Drainage Pattern Refers To The Pattern Of The Entire River Network And Should Not Be Confused With Channel Pattern Or Form, Which Refers To Limited Reaches Of Channels Or Channel Systems With More Or Less Uniform Morphological Characteristics.
Domes, Volcanic Cones, Isolated Conical Hills.
Distribution Of Stream Courses And Their Spatial Relationship To One Another.
This Pattern Is Typical In The Western And Southwestern Portions Of The United States Where Basins Exhibit Interior Drainage.
Related Post: