How Are Rain Patterns Different Near Warm And Cold Fronts
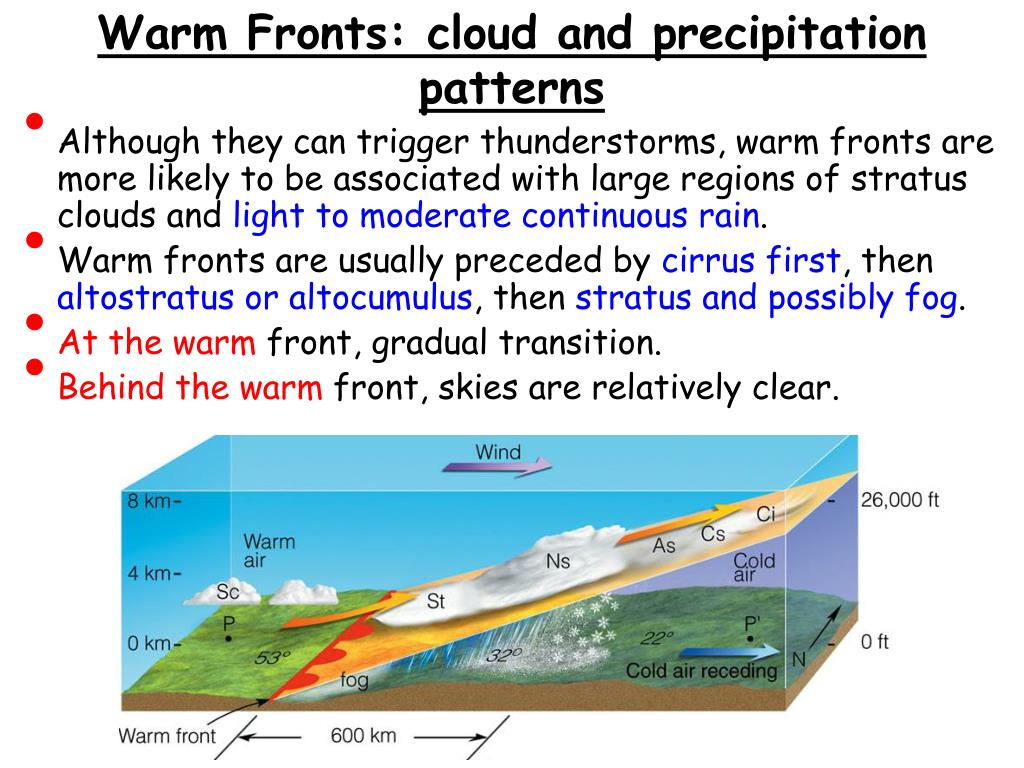
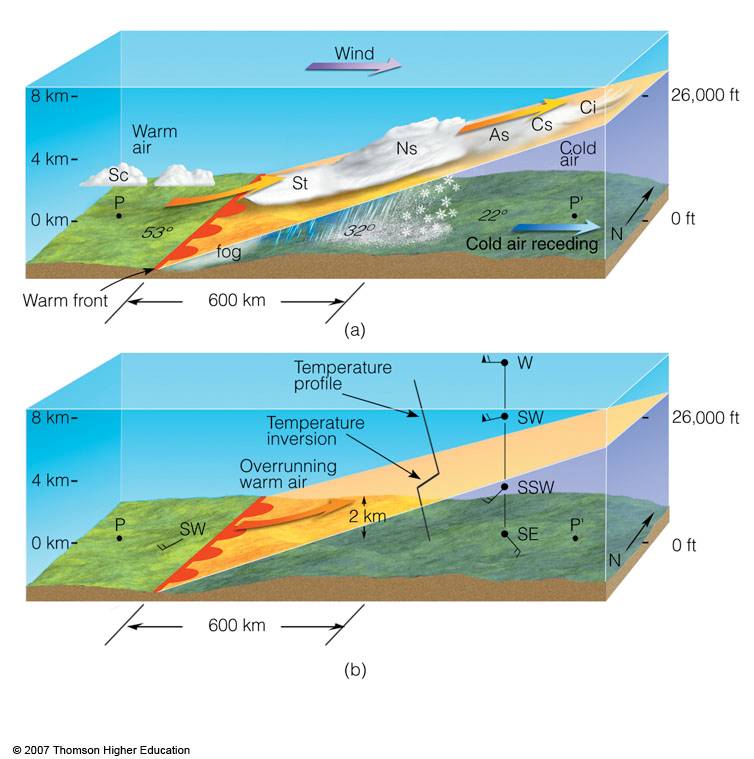
How Are Rain Patterns Different Near Warm And Cold Fronts - The precipitation associated with warm fronts is usually light to moderate, spread out over a large area. Moderate rain can form in multiple rain bands parallel to the front. Rain, snow, cold days, hot days, and windy days. Web this clashing of air types causes weather: The defined pattern of rain is determined by the movement. Accurate tracking and analysis of these fronts enable. Why does rain occur near a cold front? Web surface fronts are the boundaries or transition zones between air masses at the earth’s surface. They form when cold air moves in and forces warm air out of its way. These show where the cold air mass is wedging under the warm air mass. Accurate tracking and analysis of these fronts enable. Web a cold front leads to short, intensive rain showers while a warm front creates long, milder rain. Web cold fronts usually bring cool temperatures and heavy rain or thunderstorms. Web on a weather map, a stationary front is usually drawn using alternating cold front and warm front symbols. Web surface fronts are the boundaries or transition zones between air masses at the earth’s surface. The precipitation associated with warm fronts is usually light to moderate, spread out over a large area. A warm front is formed when a warm air mass moves into a cold air mass. Changes in temperature, humidity, wind, pressure, visibility, as well as. Warm air warm front air 1600 km arm and cold front. The defined pattern of rain is determined by the movement. Web this clashing of air types causes weather: Web cold fronts usually bring cool temperatures and heavy rain or thunderstorms. A) rain near a cold front occurs over a smaller spatial area and is less intense than near a warm front. Two major types of fronts are cold fronts and warm fronts. Warm fronts occur more slowly, provide. Winds usually blow parallel to the front, but in opposite directions. Web nimbostratus clouds cause large areas of drizzle and light continuous rain. 86 76 80 78 85. Web rain occurs along and behind a cold front. Warm fronts generally bring low ceilings, poor visibility, and rain. Warm air warm front air 1600 km arm and cold front. They form when cold air moves in and forces warm air out of its way. In an occluded front, a warm front overtakes a. Two major types of fronts are cold fronts and warm fronts. Web in a nutshell, a cold front is normally characterized by the abrupt arrival. Winds usually blow parallel to the front, but in opposite directions. The precipitation associated with warm fronts is usually light to moderate, spread out over a large area. How are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? Web how are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? Web rain near a warm front occurs over a wider spatial. Warm air warm front air 1600 km arm and cold front. Web rain near a warm front occurs over a wider spatial area and is less intense than near a cold front. They form when cold air moves in and forces warm air out of its way. As the warm air is lifted along. Two major types of fronts are. A) rain near a cold front occurs over a smaller spatial area and is less intense than near a warm front. Web how are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? Web warm fronts, cold fronts, occluded fronts, and stationary fronts all result in different types of weather patterns and precipitation. Web rain occurs along and behind a cold. How are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? 86 76 80 78 85. Web a cold front leads to short, intensive rain showers while a warm front creates long, milder rain. Web this clashing of air types causes weather: Cold fronts often bring quickly. Winds usually blow parallel to the front, but in opposite directions. The pressure reaches a relative. Web how are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? How are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? After several days, the front will likely break apart. Moderate rain can form in multiple rain bands parallel to the front. In an occluded front, a warm front overtakes a. Web cold fronts warm fronts. Web rain near a warm front occurs over a wider spatial area and is less intense than near a cold front. Why does rain occur near a cold front? Web cold fronts are boundaries between cold and warm air masses. Web rain occurs along and behind a cold front. How are rain patterns different near warm and cold fronts? Why does rain occur near a cold front? Rising warm air cools, resulting in. As the warm air is lifted along. 85 82 80 60 67 52 78. Web at a cold front, a cold air mass forces a warm air mass upwards. Web rain near a warm front occurs over a wider spatial area and is less intense than near a cold front. Web on a weather map, a stationary front is usually drawn using alternating cold front and warm front symbols. Web cold fronts warm fronts. Web a stationary front may bring days of rain, drizzle, and fog. For example, one air mass may be cold and dry and the other air. Web cold fronts are boundaries between cold and warm air masses. 67 61 65 68 62 54 85. Web in a nutshell, a cold front is normally characterized by the abrupt arrival of stormy, rainy weather that makes a significant impact on a region. After several days, the front will likely break apart. Why does rain occur near a cold front? Moderate rain can form in multiple rain bands parallel to the front. A warm front is formed when a warm air mass moves into a cold air mass. Rising warm air cools, resulting in.Section 1 Weather Patterns Nitty Gritty Science
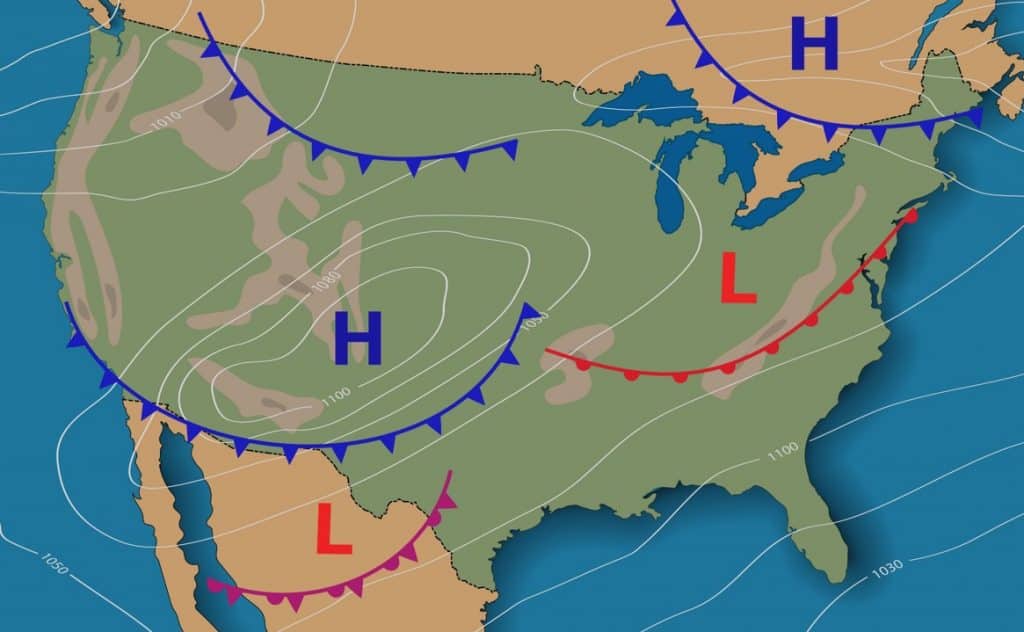
LABORATORY 4 MIDLATITUDE CYCLONES, WEATHER MAPS, AND FORECASTING
PPT Air Masses and Fronts II PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Paddle Smart Weather Page
Biosphere, Atmosphere and Hydrosphere Types of rainfall
Climate Prediction Center El Niño Temperature and Precipitation Patterns
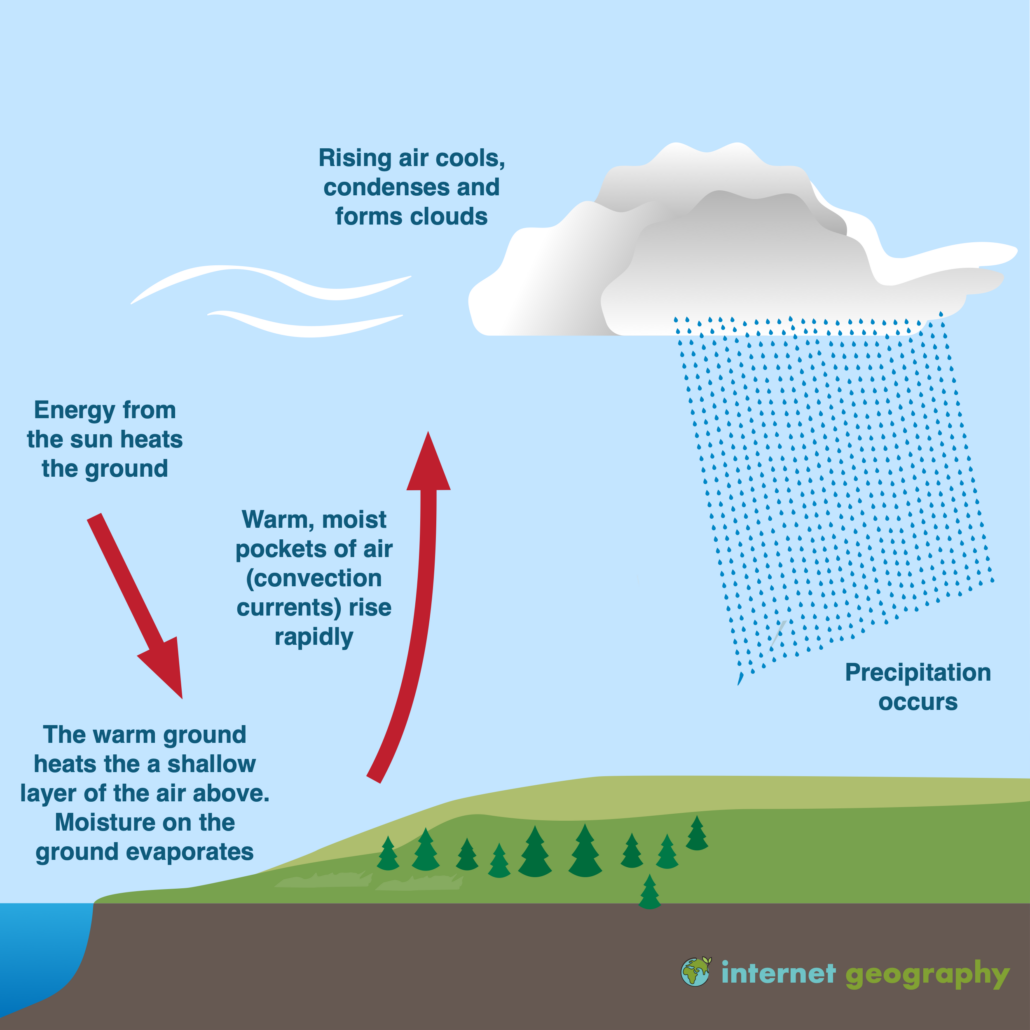
What is convectional rainfall? Geography
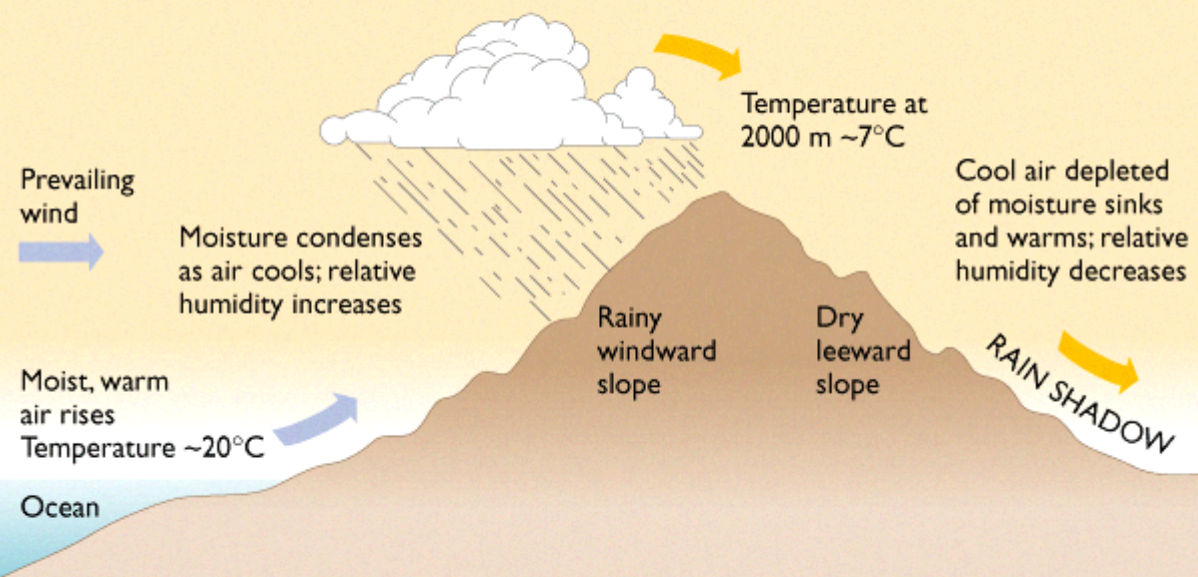
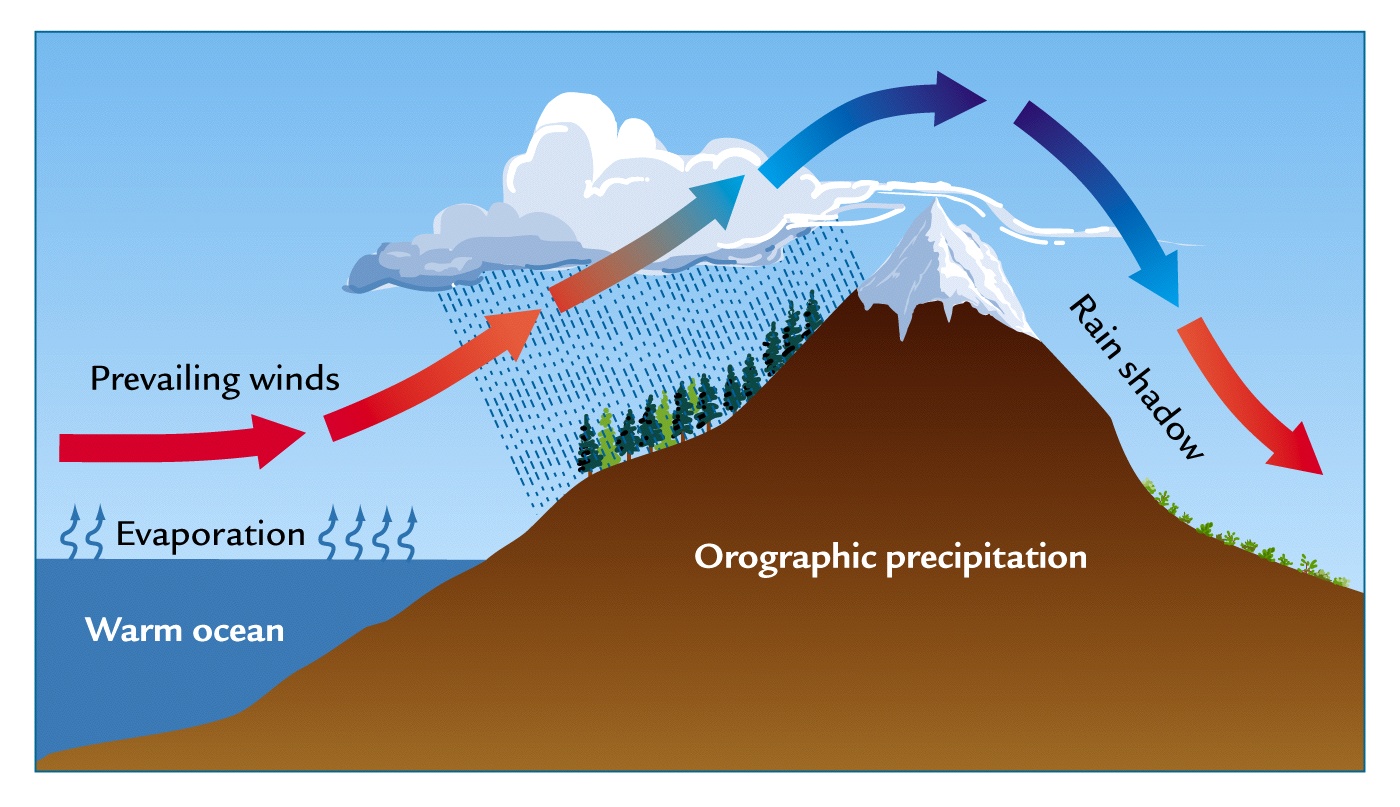
Brian Blaylock's Weather Blog Orographic Precipitation
h2g2 Fronts, Depressions and Anticyclones
Orographic precipitation Definition, Cause, Location, & Facts
Warm Fronts Occur More Slowly, Provide.
Stationary Fronts Bring Long Rainy Periods That Stay In One.
At A Warm Front, The Warm Air Mass Slips Above The Cold Air Mass.
In An Occluded Front, A Warm Front Overtakes A.
Related Post: