Si Joint Referred Pain Patterns
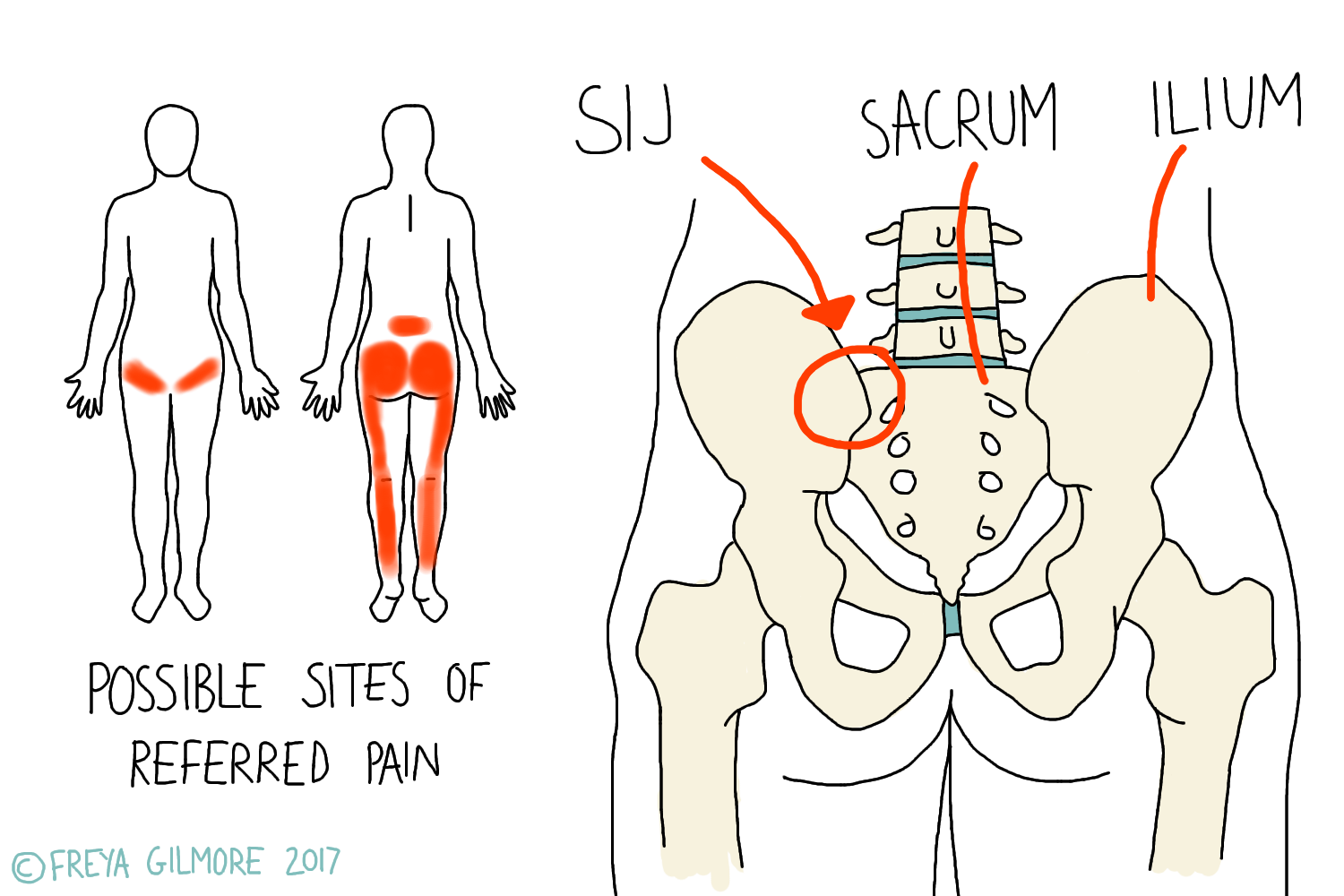
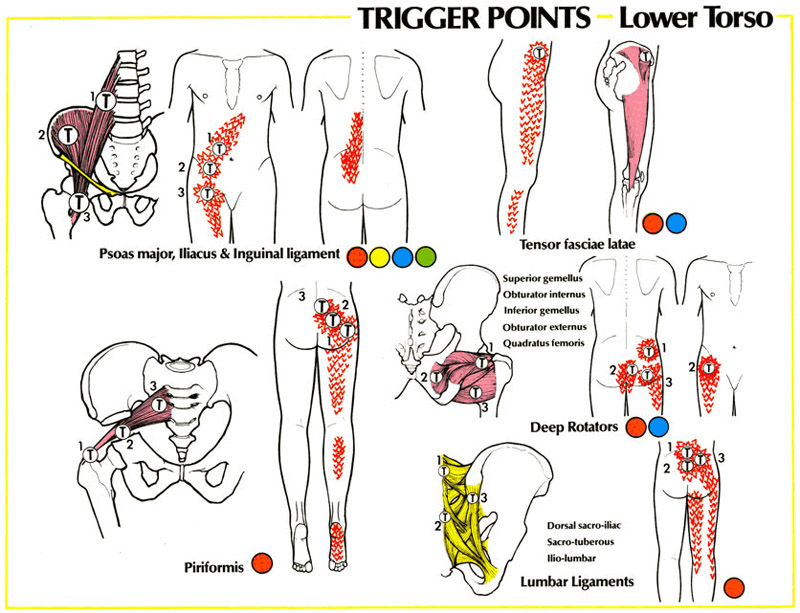
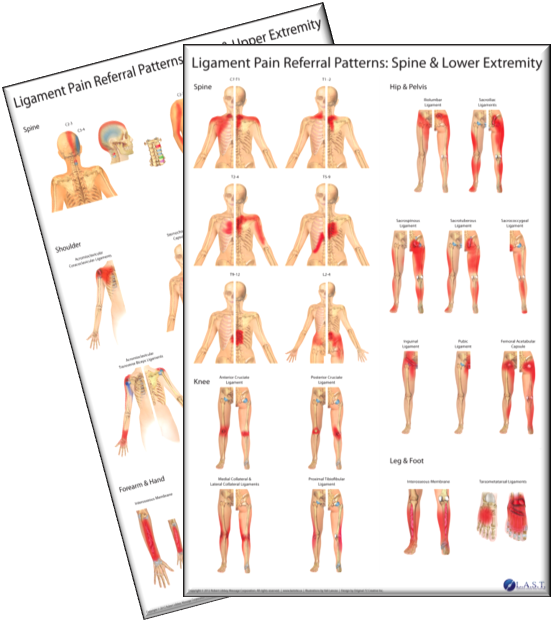
Si Joint Referred Pain Patterns - Sacroiliac joint pain can be from trauma, pregnancy, repetitive stress, sports, and following spinal surgery. 28% experienced pain extending below the knee. The sacroiliac (si) joint, a vital connection between the spine and pelvis, plays a key role in load distribution and spinal stability. Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and the. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and treatment of sij disorders. These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. Web si joint pain is commonly referred to the buttocks, lower lumbar region, groin, and lateral thigh. 72% reported lower lumbar pain. Patients with sacroiliac joint dysfunction describe their pain being aggravated by getting out of a chair, prolonged standing or sitting, with climbing stairs or. This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and treatment of sij disorders. Fifty consecutive patients who satisfied clinical criteria and demonstrated a positive diagnostic response to a fluoroscopically guided sacroiliac joint injection were included. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and the. Web si joint pain is commonly referred to the buttocks, lower lumbar region, groin, and lateral thigh. In reality, only the anterior third of the interface between the sacrum and ilium is a true synovial joint; Web sacroiliitis is an inflammation of one or both of the sacroiliac (si) joints, most often resulting pain in the lower back that can extend down the legs. These patterns are discussed in greater detail later in this text (see chapters 14 to 18 ). The rest of the junction is comprised of an intricate set of ligamentous connections. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and the. Typically, referred pain is described as dull, aching, gnawing, annoying, drilling, or pressing (1, 55). Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction is a common cause of low back pain and accurate diagnosis can be challenging. Web referred pain usually occurs after local pain has persisted for a. These patterns are discussed in greater detail later in this text (see chapters 14 to 18 ). These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. Pain arising from the sacroiliac joint is one of the potential causes of axial low back pain. Fifty consecutive patients who satisfied clinical criteria and demonstrated a positive diagnostic response to a fluoroscopically. Web characterize the pain referral patterns of patients with sijs who demonstrated a positive response to a fluoroscopically guided diagnostic sacroiliac joint injection. A complete history and physical examination are critical in differentiating other. These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. Fifty consecutive patients who satisfied clinical criteria and demonstrated a positive diagnostic response to a fluoroscopically. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction is a common cause of low back pain and accurate diagnosis can be challenging. A complete history and physical examination are critical in differentiating other. Learn more about the symptoms, causes, and treatment of si joint pain. In reality, only the anterior third of the interface between the sacrum and ilium is a true synovial. Fifty consecutive patients who satisfied clinical criteria and demonstrated a positive diagnostic response to a fluoroscopically guided sacroiliac joint injection were included. Web sacroiliac (si) joint dysfunction describes pain due to abnormal movement (too much or too little) or misalignment of the si joint. Other potential contributors include spinal scoliosis, leg length discrepancy, and previous lumbar spine fusion. These joints. Patients with sacroiliac joint dysfunction describe their pain being aggravated by getting out of a chair, prolonged standing or sitting, with climbing stairs or. Typically, referred pain is described as dull, aching, gnawing, annoying, drilling, or pressing (1, 55). Web pain from the sij is localized to an area of approximately 3 cm × 10 cm that is inferior to. Sacroiliac joint pain can be from trauma, pregnancy, repetitive stress, sports, and following spinal surgery. Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. Web sacroiliac joint pain is among the most common causes of. Web found a composite area of 3 × 10 cm, just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine (psis), interpreted as specific for si joint pain. 28% experienced pain extending below the knee. Web sij dysfunction generally refers to aberrant position or movement of sij structures that may or may not result in pain. Adjacent structures, such as the piriformis. A complete history and physical examination are critical in differentiating other. Sometimes, referred pain is associated with secondary hyperalgesia and trophic changes. In reality, only the anterior third of the interface between the sacrum and ilium is a true synovial joint; Web found a composite area of 3 × 10 cm, just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine (psis),. Fifty consecutive patients who satisfied clinical criteria and demonstrated a positive diagnostic response to a fluoroscopically guided sacroiliac joint injection were included. The rest of the junction is comprised of an intricate set of ligamentous connections. Web 11 min read. This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and treatment. Other potential contributors include spinal scoliosis, leg length discrepancy, and previous lumbar spine fusion. These patterns are discussed in greater detail later in this text (see chapters 14 to 18 ). Web the variable patterns of pain referral observed may arise for several reasons, including the joint's complex innervation, sclerotomal pain referral, irritation of adjacent structures, and varying locations of injury with the sacroiliac joint. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (si joint). The rest of the junction is comprised of an intricate set of ligamentous connections. Web sacroiliitis is an inflammation of one or both of the sacroiliac (si) joints, most often resulting pain in the lower back that can extend down the legs. Web sacroiliac joint pain is among the most common causes of low back pain. This paper aims to clarify the difference between these clinical concepts and present current available evidence regarding diagnosis and treatment of sij disorders. Sometimes, referred pain is associated with secondary hyperalgesia and trophic changes. Fifty consecutive patients who satisfied clinical criteria and demonstrated a positive diagnostic response to a fluoroscopically guided sacroiliac joint injection were included. A quarter of low back pain could be originating from the sacroiliac joint [1]. The sacroiliac (si) joint, a vital connection between the spine and pelvis, plays a key role in load distribution and spinal stability. 72% reported lower lumbar pain. Web pain from the sij is localized to an area of approximately 3 cm × 10 cm that is inferior to the ipsilateral posterior superior iliac spine. 50% felt pain in the lower extremities. Using this area as reference, this was confirmed in a second study in chronic lbp patients suspected of having si joint pain.Typical Pain Referral Pattern Of Sacroiliac Joint Pai vrogue.co
Pain referral from the sacroiliac joint. Van der Wurff et al., 2006 [33
Sacroiliac Joint Pain Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
The Sacroiliac Joint (SIJ) Beth Forrest Osteopathy
Typical pain referral pattern of sacroiliac joint pain (illustration
Sacroiliac Joint Referred Pain
The Referral Patterns of the Sacroiliac Joint, Facet Joints, and
Si Joint Pain Referral Patterns
Sciatica GadiBody
Sacroiliac Joint Referred Pain
Web Pain Patterns Of The Chest, Back, Shoulder, Scapula, Pelvis, Hip, Groin, And Sacroiliac (Si) Joint Are The Most Common Sites Of Referred Pain From A Systemic Disease Process.
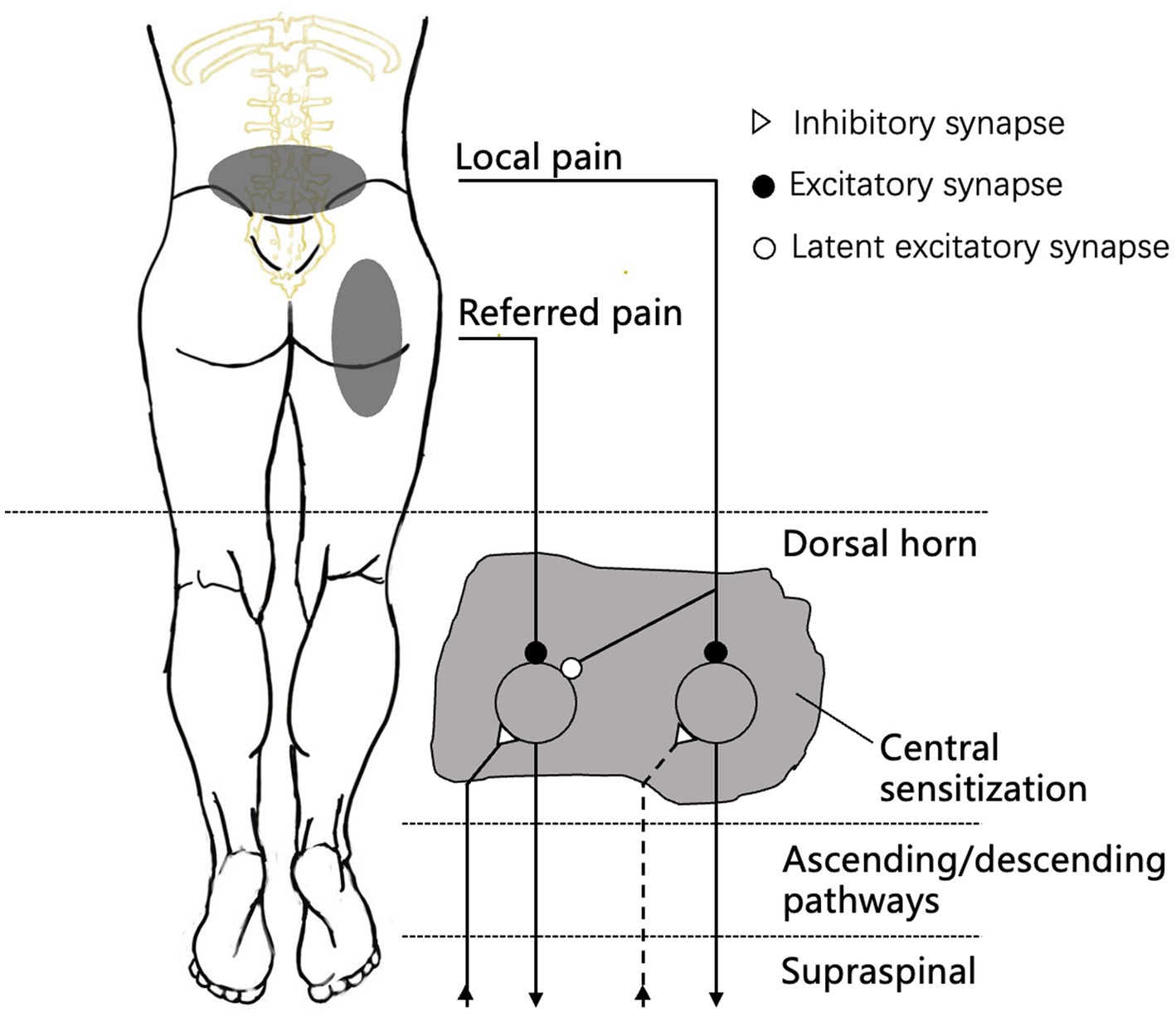
Web Referred Pain Usually Occurs After Local Pain Has Persisted For A Certain Period (5, 55).
Web Si Joint Pain Is Commonly Referred To The Buttocks, Lower Lumbar Region, Groin, And Lateral Thigh.
In Reality, Only The Anterior Third Of The Interface Between The Sacrum And Ilium Is A True Synovial Joint;
Related Post:


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sacroiliac-joint-pain-189250-V1-5d9c0b81b3294cb69347d22ef581d05d.jpg)